Nutrition in Living Organisms-Animals and Man
A. Fill in the blanks.
- The digestion of food in humans starts in the Buccal cavity and is completed in the anus.
- Hydrochloric acid present in the stomach, kills bacteria.
- The largest gland in the human body is the liver.
- Partially digested food, that is chewed again by grass eating animals, is called cud.
- Amoeba uses pseudopodia for locomotion and for capturing its food.
B. Match the following:
Ans.
1. Gall bladder | (a) Bile Juice |
2. Proteins | (e) Amino acids |
3. Intestinal wall | (c) Absorption |
4. Rumen | (b) Cow |
5. Pseudopodia | (d) False feet |
C. Tick (✓) the correct option.
1.Organisms that can synthesise their own food are called—
☐ heterotrophs
☐ parasites
✅ autotrophs
☐ saprotrophs
2.Cow is a/an—
☐ saprotroph
☐ parasite
☐ autotroph
✅ heterotroph
3.Animals, that eat both plant materials and animals, are called—
☐ herbivores
✅ omnivores
☐ carnivores
☐ ruminants
4.Which one of these is not a part of the alimentary canal?
☐ stomach
☐ anus
✅ liver
☐ large intestine
5.Bile juice is released by the—
☐ salivary glands
☐ pancreas
✅ liver
☐ large intestine
D. Answer the following questions in brief
1.Define the following terms:
(a) Holozoic nutrition
Ans.
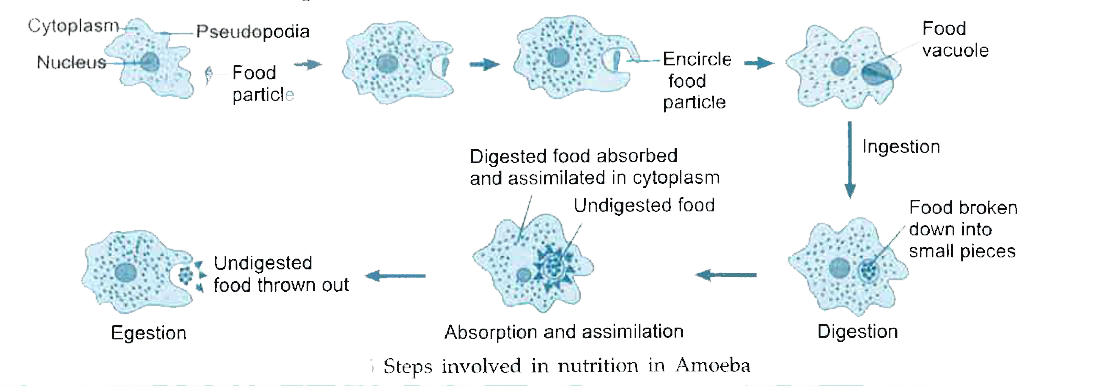
Holozoic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms eat solid or liquid food and then it is broken down (or digested) to provide the required nutrition to the body.
Example: Humans, Amoeba
(b) Alimentary canal
Ans.
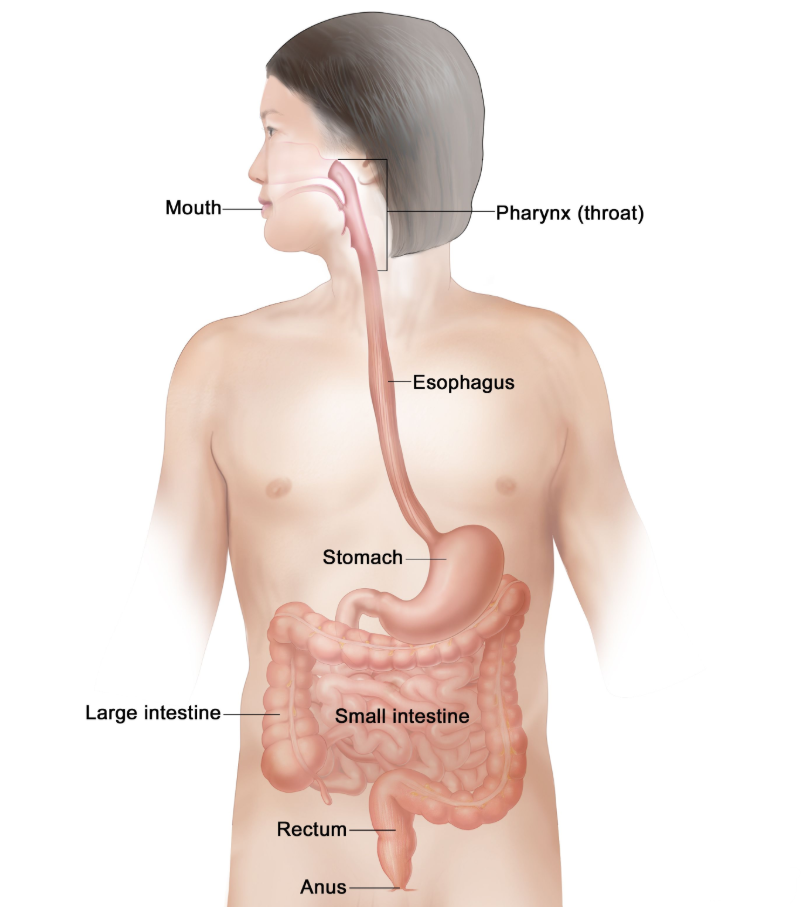
The alimentary canal is a long, muscular tube in our body through which food passes. It starts from the mouth and ends at the anus. It helps in the digestion, absorption, and removal of undigested food.
It includes parts like: buccal cavity, oesophagus (food pipe), stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus.
2.Give the meaning of the terms:
(a) Assimilation
Ans.
Assimilation is the process by which the absorbed food is used by the body for growth, repair, and energy.
It happens after digestion and absorption.
Example: The glucose from digested food is used by our muscles to produce energy.
(b) Rumination
Ans.
Rumination is the process by which grass-eating animals, like cow, deer, camel bring back partially digested food from the stomach to the mouth to chew it again. These animals are called ruminants, and the food they bring back is called cud.
3.Name the organs that make up the human alimentary canal.
Ans.
The main organs that make up the human alimentary canal are buccal cavity, oesophagus (food pipe), stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus.
4.State two differences between milk teeth and permanent teeth.
Ans.
Feature | Milk Teeth | Permanent Teeth |
Number of teeth | 20 | 32 |
Timing and longevity | Erupt around 6 months; shed by age 12 | Begin erupting around age 6; last for life |
5.Name the four types of teeth in the human mouth.
Ans.
The four types of teeth in the human mouth are:
- Incisors – used for cutting food
- Canines – used for tearing food
- Premolars – used for crushing and grinding food
- Molars – used for grinding and chewing food
6.State the function of the (a) incisor teeth, (b) premolar teeth.
Ans.
(a) Incisor teeth: Used for cutting and biting food.
(b) Premolar teeth: Used for crushing and grinding food.
7.State the role of acid in the human stomach.
Ans.
The role of acid (hydrochloric acid) in the human stomach are :
- Killing germs: It destroys many harmful microorganisms present in the food.
- Creating an acidic environment: Provides the right acidic medium for digestive enzymes to work effectively.
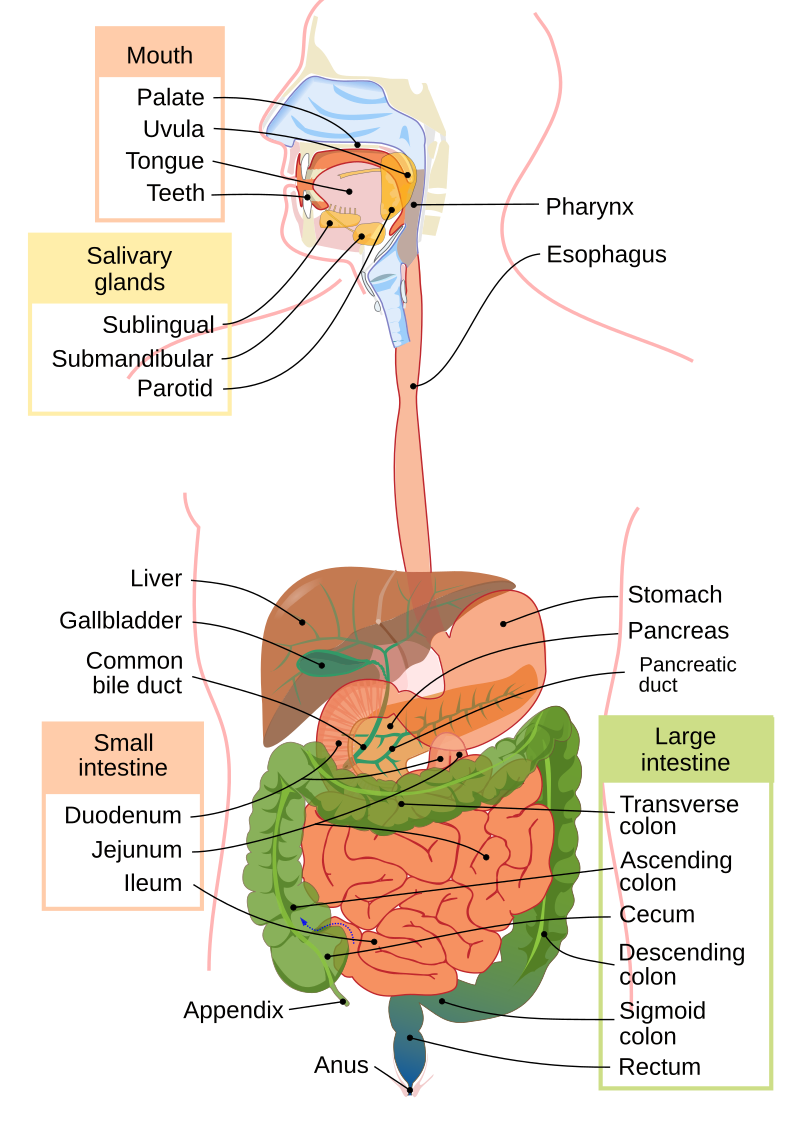
8.State the function of (a) bile juice and (b) pancreatic juice in the human digestive system.
Ans.
(a) Bile juice:
Bile juice helps in the digestion of fats. It is made by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile breaks large fat droplets into smaller ones so that enzymes can digest the fats more easily.
(b) Pancreatic juice:
Pancreatic juice contains enzymes that help digest carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It is made by the pancreas and released into the small intestine, where it breaks down food into simpler forms.
E. Answer the following questions.
1.Draw a neat, well-labelled diagram of the human digestive system.
Ans.
2.Justify the following statements:
(a) Crow is an omnivore.
Ans.
A crow is called an omnivore because it eats both plant-based food (like fruits, grains, and seeds) and animal-based food (like insects and dead animal remains).
(b) It is said that the mode of nutrition, in human beings and Amoeba, is quite similar.
Ans.
The mode of nutrition in both human beings and Amoeba is called holozoic nutrition. The basic steps of ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion are present in both, making their modes of nutrition quite similar.
3.Give reasons for the following:
(a) Ingestion of food is difficult without teeth.
Ans.
Teeth help in biting, cutting, tearing, and grinding food into smaller pieces. Without teeth, it is difficult to swallow and digest the food properly.
(b) If we chew rice, or bread, for a few minutes, it starts tasting sweet.
Ans.
Rice and bread contain starch, a complex carbohydrate. When we chew them, saliva mixes with the food and breaks down starch into simpler sugars like maltose. These simpler sugars taste sweet.
(c) Bacteria are present in the caecum of ruminants.
Ans.
Ruminants (like cows and buffaloes) eat a lot of cellulose-rich plant material (e.g. grass). The caecum in their digestive system contains special bacteria that produce enzymes to break down cellulose, which animals cannot digest on their own.
4.Explain how digested food gets absorbed into the blood.
Ans.
Once the food is fully digested, it is taken into the blood so it can reach all parts of the body. This is called absorption. It happens mainly in the small intestine. The inner wall of the small intestine has tiny finger-like structures called villi, which help increase the surface area so that more food can be absorbed quickly. The villi have thin walls and contain many small blood vessels to take the digested food into the blood.
5.State, in one/two sentence/s each, the various processes involved in nutrition in ruminant animals.
Ans.
Ingestion – Ruminants eat plant material like grass and swallow it quickly.
Rumination – The swallowed food is stored in the rumen and later brought back to the mouth for chewing again (chewing the cud).
Digestion – Microorganisms in the rumen help break down tough plant parts like cellulose.
Absorption – Digested food moves to the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed into the blood.
Egestion – The undigested waste is removed from the body through the anus.
6.Explain ingestion of food, in Amoeba, through a diagram.
Ans.